BRICSEXPANSION
Formation and Evolution
The concept of BRICS originated from a 2001 report by Jim O’Neill of Goldman Sachs, who coined the term “BRIC” to describe the emerging markets of Brazil, Russia, India, and China.
The formal establishment of BRIC as a group occurred in 2006 when the foreign ministers of Brazil, Russia, India, and China met on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly. This meeting set the stage for further cooperation, leading to the first BRIC summit in Yekaterinburg, Russia, in 2009. The primary agenda of this summit was to enhance cooperation and discuss measures to reform global financial institutions to reflect the growing influence of emerging economies.
In 2010, South Africa was invited to join the group, resulting in the expansion of BRIC to BRICS. The inclusion of South Africa was significant as it added a representative from the African continent, thus increasing the group’s geographical diversity and political clout.
Objectives and Goals
BRICS was formed with several overarching goals, including:
- Promoting peace, security, and development.
- Enhancing economic cooperation and trade among member countries.
- Reforming global financial institutions to reflect the economic weight of emerging markets.
- Strengthening political and diplomatic coordination on international issues.
- Facilitating mutual support in financial matters and sustainable development.
The group’s annual summits provide a platform for dialogue and collaboration, allowing BRICS nations to coordinate their policies and initiatives on a wide- range of global issues, from economic growth and trade to climate change and security.
Political and Strategic Importance of BRICS
BRICS is not only an economic alliance but also a significant political and strategic coalition. The group’s political and strategic importance is multifaceted, influencing global governance, geopolitics, and international relations.
- Alternative Power Bloc: BRICS serves as a counterbalance to Western-dominated institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the World Bank, and the Group of Seven (G7). By promoting a multipolar world, BRICS aims to reduce the dominance of Western powers in global affairs.
- Reform of Global Institutions: BRICS advocates the reform of global financial and political institutions to ensure fair representation of emerging economies. This includes pushing for greater voting rights in the IMF and the World Bank.
- UN and G20: BRICS countries collectively influence major international organizations, including the United Nations (UN) and the G20. Their coordinated stances on key issues enhance their negotiating power and impact on global policies.
- Common Positions: The group often takes unified positions on critical global issues such as climate change, terrorism, and sustainable development, thereby amplifying their collective voice in international forums.
- Conflict Resolution: BRICS countries engage in diplomatic efforts to resolve regional conflicts and promote global stability. Their involvement in peacekeeping and mediation efforts is crucial in various geopolitical hotspots.
- Security Cooperation: BRICS members collaborate on security issues, sharing intelligence and coordinating efforts to combat terrorism, cyber threats, and other security challenges.
- Trade and Investment: Enhanced economic ties among BRICS countries bolster their collective economic strength and reduce dependence on traditional Western markets. This is achieved through initiatives like the BRICS Business Council and the annual BRICS Trade Fair.
- Strategic Partnerships: The group fosters strategic partnerships in areas such as defence, technology, and energy. These partnerships help BRICS countries leverage their strengths and enhance their strategic autonomy.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): BRICS countries are committed to achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. They cooperate on projects that promote sustainable development, poverty alleviation, and environmental protection.
- Renewable Energy: Collaborative efforts in renewable energy development are a key focus area. BRICS countries share technology and expertise to promote clean and sustainable energy sources.
- People-to-People Ties: BRICS promotes cultural exchange and people-to-people ties among member countries. This fosters mutual understanding and strengthens the social fabric of the group.
- Educational Cooperation: Joint research initiatives, academic exchanges, and educational partnerships enhance knowledge sharing and innovation among BRICS nations.
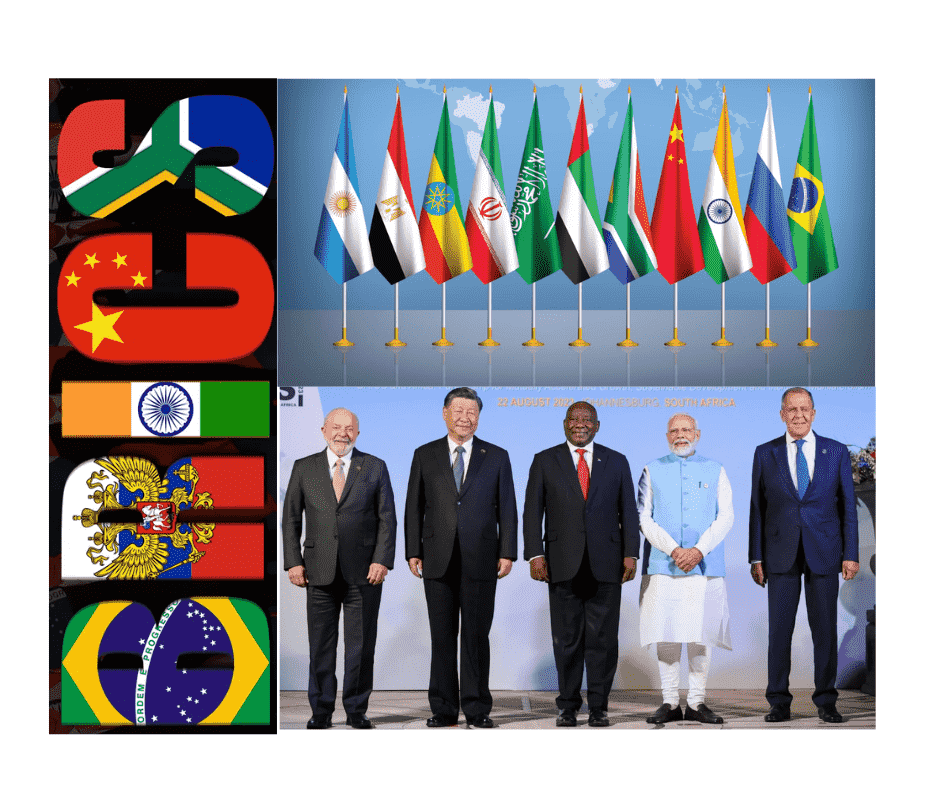
BRICS Expansion: A Strategic Move to Challenge Western Dominance?
In a significant development aimed at increasing its influence in global affairs, the BRICS bloc, comprising top emerging economies like Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa has announced in January, 2024 the inclusion of five new full members. The expansion marks a strategic move to bolster the group’s clout amidst a backdrop of Western dominance in world affairs. As Moscow assumed the presidency of BRICS, Russian President Vladimir Putin confirmed the addition of Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to the bloc, transforming BRICS into a 10-nation body.
Strengthening Global Influence
The induction of the five new members reflects BRICS’ commitment to broadening its reach and enhancing its strategic importance on the global stage. By welcoming Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, BRICS is not only expanding its geographical footprint but also diversifying its economic and political influence. This move signals the group’s ambition to play a more prominent role in shaping a multipolar world order.
BRICS has long championed the principles of sovereign equality, openness, and consensus. These foundational values resonate with many countries that seek to challenge the existing Western-dominated global financial and trading systems. The inclusion of the new members underscores BRICS’ appeal to nations that share its vision of a fairer and more balanced international order.
Enhanced Strategic Heft
The expanded BRICS bloc is poised to leverage the combined strengths of its new and existing members to push for reforms in global governance structures. The addition of resource-rich and strategically located countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE enhances the group’s economic leverage, particularly in energy markets. Meanwhile, the inclusion of Egypt and Ethiopia brings significant geopolitical weight to the African continent, and Iran’s membership introduces a critical voice from the Middle East.
This enlargement of BRICS is expected to boost intra-bloc trade and investment, fostering greater economic integration among member countries. It also opens up new avenues for cooperation in areas such as infrastructure development, technology transfer, and cultural exchange.
A Multipolar Vision
President Putin emphasized that the growing membership of BRICS reflects its increasing attractiveness to like-minded countries worldwide. “BRICS is attracting an ever-increasing number of supporters and like-minded countries that share its underlying principles such as sovereign equality, openness, consensus, aspiration to form a multipolar international order, and a fair global financial and trading system,” he noted.
As BRICS continues to expand, it is clear that the bloc aims to challenge the existing power dynamics in international relations. The group’s efforts to promote a multipolar world order are aligned with the aspirations of many countries that seek greater representation and fairness in global decision-making processes.
Major Achievements of BRICS:
Since its inception, the BRICS grouping (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) has made substantial contributions to global economic, political, and social landscapes. These achievements highlight the bloc’s growing influence and its commitment to promoting a multipolar world order. Here are some of the major achievements of BRICS:
- Establishment of the New Development Bank (NDB)
Creation and Purpose: In 2014, BRICS launched the New Development Bank (NDB) to fund infrastructure and sustainable development projects in BRICS countries and other emerging economies. The NDB provides an alternative to traditional financial institutions like the World Bank and IMF.
Impact: The NDB has approved billions of dollars in funding for various projects, including renewable energy, transportation, and urban development. This funding supports economic growth and development in member countries and beyond.
Financial Stability Mechanism: Alongside the NDB, BRICS established the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) in 2014. The CRA is designed to provide liquidity support to member countries during balance of payments crises or currency instability.
Significance: The CRA enhances financial stability among BRICS nations, offering a collective financial safety net and reducing reliance on traditional Western-dominated financial systems.
- Annual BRICS Summits and Declarations
Policy Coordination: BRICS holds annual summits where leaders discuss key global and regional issues, economic cooperation, and political strategies. These summits produce joint declarations that outline common positions and future initiatives.
Global Influence: Through these coordinated efforts, BRICS has influenced major international policies on issues such as climate change, global security, and sustainable development.
- Growth in Intra-BRICS Trade and Investment
Economic Integration: Trade and investment flows among BRICS countries have increased significantly, driven by efforts to reduce trade barriers and enhance economic cooperation. This has diversified markets and reduced reliance on traditional trading partners.
Investment Initiatives: Strategic investments in sectors like infrastructure, technology, and energy have bolstered economic ties and supported development across member states.
- Establishment of the BRICS Business Council
Private Sector Engagement: The BRICS Business Council was created to promote business cooperation among member countries. It provides a platform for dialogue between the private sector and BRICS governments, fostering trade and investment.
Initiatives and Forums: The council has launched initiatives like the annual BRICS Business Forum and sector-specific working groups, which enhance business ties and economic collaboration.
- Launch of the BRICS Network University
Academic Cooperation: Established in 2015, the BRICS Network University facilitates academic and research collaboration among universities in BRICS countries. It focuses on priority areas such as energy, computer science, and climate change.
Joint Research Projects: The network has promoted joint research initiatives, academic exchanges, and educational partnerships, enhancing knowledge sharing and innovation among BRICS nations.
- Cultural and Social Initiatives
People-to-People Exchanges: BRICS has promoted cultural exchange and mutual understanding through initiatives like the BRICS Film Festival, BRICS Games, and various academic exchange programs.
Youth Engagement: Programs targeting youth, such as the BRICS Youth Summit and scholarship schemes, have fostered greater connectivity and understanding among the younger generations of member countries.
- Technological and Innovation Cooperation
BRICS Innovation Network: The BRICS Innovation Network promotes collaboration in research and development, innovation, and technology transfer. This network harnesses the technological strengths of each member country to drive economic growth.
Joint Tech Projects: Collaborative projects in areas such as artificial intelligence, space exploration, and renewable energy highlight the group’s commitment to leveraging technology for mutual benefit.
- Health and Pandemic Response
COVID-19 Cooperation: During the COVID-19 pandemic, BRICS countries collaborated on public health responses, sharing best practices, medical supplies, and vaccine development efforts.
Health Research: BRICS has strengthened joint research initiatives on public health issues, aiming to enhance the healthcare systems of member countries and improve global health security.
BRICS Foreign Ministers Meet (10-11 June 2024) in Russia: Key Outcomes and Strategic Moves
The BRICS nations recently gathered in Nizhny Novgorod, Russia, on June 10th and 11th, 2024, for a significant meeting of their foreign ministers. This gathering highlighted the group’s ongoing commitment to enhancing cooperation and tackling global challenges together. Here’s a closer look at what was discussed and the key outcomes of the meeting.
Embracing Local Currencies
One of the hot topics on the agenda was the push to use local currencies more in trade and financial transactions among BRICS countries. This move aims to reduce their reliance on major global currencies, giving them more economic independence and making trade within the group smoother and more efficient.
Supporting Africa and Palestine
The BRICS nations reaffirmed their support for peace efforts in Africa, standing by the principle of “African solutions to African problems.” They emphasized the importance of backing the African Union and other regional organizations in their efforts to maintain peace and resolve conflicts.
In a show of solidarity, BRICS also threw its weight behind Palestine’s bid for full membership in the United Nations. The ministers reiterated their commitment to a two-state solution, urging for the implementation of measures to ensure a ceasefire in Gaza and calling for the release of hostages and civilians.
Championing Multilateralism and UN Reform
The joint statement from the meeting underscored BRICS’ commitment to multilateralism and adherence to international law, particularly the principles enshrined in the United Nations Charter. The foreign ministers called for comprehensive reforms of the UN, especially making the Security Council more democratic and representative.
Boosting the G20 and African Union
The ministers highlighted the G20’s crucial role in international economic cooperation and welcomed the African Union’s new status as a G20 member, which was announced at the G20 New Delhi Summit. They expressed support for the upcoming G20 presidencies of India, Brazil, and South Africa, aiming to address global economic inequalities.
Addressing Global Conflicts
The BRICS ministers expressed deep concern over ongoing global conflicts, specifically mentioning the situations in Ukraine and the Occupied Palestinian Territory. They condemned the violence in Gaza and called for measures to ensure a lasting ceasefire. The group emphasized the importance of peaceful conflict resolution and international law.
Fighting Terrorism
In a strong statement, the BRICS ministers condemned all forms of terrorism, stressing the need for zero tolerance towards such acts. They called for accountability for those involved in terrorist activities and highlighted the importance of ensuring that Afghanistan does not become a haven for terrorists.
Tackling Climate Change and Trade Barriers
The ministers reiterated the urgency of implementing the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement. They opposed protectionist trade measures that disrupt global supply chains and supported a fair, rules-based trading system that benefits developing countries.
Advocating WTO Reform
BRICS also voiced their support for a transparent and inclusive World Trade Organization (WTO). They called for reforms to strengthen the WTO’s effectiveness and ensure that developing countries receive special treatment to support their growth.
Future Prospects and Challenges of BRICS:
As the BRICS bloc—comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—continues to solidify its place in global affairs, it faces a spectrum of both promising opportunities and formidable challenges on the horizon.
Opportunities for Growth and Influence
Economic Expansion: BRICS economies collectively represent a significant portion of global GDP and trade. The bloc’s continued economic growth, fueled by domestic consumption and technological advancements, positions it as a crucial driver of global economic dynamics.
Enhanced Regional Cooperation: Initiatives like the New Development Bank (NDB) and the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) strengthen financial cooperation and resilience among member nations. These institutions provide alternative sources of funding for infrastructure projects and bolster economic stability.
Innovation and Technology: BRICS countries are at the forefront of technological innovation, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and digital economy. Collaborative efforts in research and development can lead to breakthroughs with global implications.
Challenges to Address
Geopolitical Tensions: Differences in geopolitical interests among BRICS members, compounded by global power shifts, pose challenges to cohesive decision-making and strategic alignment. Managing divergent viewpoints while maintaining unity remains critical.
Economic Disparities: Despite economic growth, disparities in development levels and income inequality within BRICS nations persist. Addressing these gaps requires inclusive growth strategies, targeted investments in human capital, and sustainable development practices.
Global Governance Reform: BRICS advocates for reforms in global governance institutions, including the United Nations and the World Trade Organization, to better reflect contemporary geopolitical realities. Overcoming resistance to reforms and achieving consensus on priorities remains a complex task.
Environmental Sustainability: Climate change poses significant challenges globally, and BRICS countries, as major emerging economies, have a pivotal role in adopting sustainable practices. Balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship requires innovative policies and international cooperation.
Security and Stability: BRICS faces security challenges ranging from terrorism and cyber threats to regional conflicts. Strengthening cooperation in counter-terrorism efforts, conflict prevention, and peacekeeping initiatives is essential for regional and global stability.
Conclusion
BRICS is at a critical point, balancing big ambitions with significant challenges. The group aims to boost economic integration, support sustainable development, and promote a fairer global order. Initiatives like the New Development Bank show their proactive approach to fostering growth and stability.
However, internal conflicts, economic disparities, and slow global reforms present hurdles. Geopolitical tensions and economic volatility further complicate their efforts. Despite these obstacles, BRICS’ focus on enhancing trade, fostering innovation, and pushing for global reforms offers a hopeful path forward.
Ultimately, the future of BRICS hinges on its ability to handle these challenges and maintain unity. With strategic collaboration and a shared vision, BRICS can continue to drive positive change and build a more balanced world.






